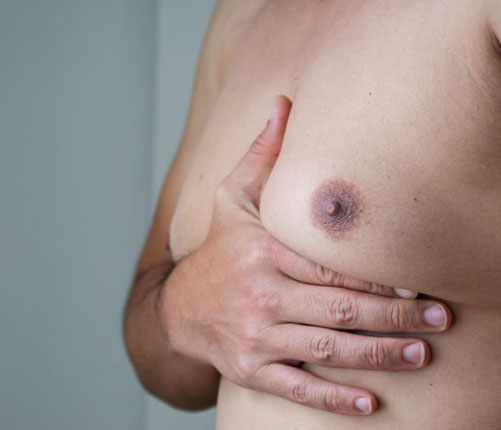
Gynecomastia, also known as male breast reduction surgery, is a procedure aimed at reducing excess breast tissue in males to achieve a flatter and more masculine chest contour.
- Operations
Real People, Real Results
Gynecomastia, also known as male breast reduction surgery, is a procedure aimed at reducing excess breast tissue in males to achieve a flatter and more masculine chest contour.
Gynecomastia can be caused by hormonal imbalances, such as fluctuations in testosterone and estrogen levels, as well as certain medications, medical conditions like liver disease, use of anabolic steroids, and sometimes during aging.
One primary cause is hormonal imbalances, where fluctuations in testosterone and estrogen levels disrupt the typical balance. Testosterone, responsible for masculine traits, can be overshadowed by elevated estrogen levels, leading to breast tissue growth.
Medications also play a significant role in triggering gynecomastia. Certain drugs, such as those used in prostate cancer treatment, anabolic steroids, some antidepressants, and medications for heartburn and ulcers, can interfere with hormone levels, contributing to breast tissue enlargement.
Besides that, some medical conditions can prompt gynecomastia. Liver disease, kidney failure, thyroid disorders, and tumors in the testes, adrenal glands, or pituitary gland may disrupt hormone balance and manifest as gynecomastia.
Gynecomastia affects approximately 65% of adult men to some extent
Studies have shown that up to 75% of men with gynecomastia report experiencing psychological distress, including feelings of embarrassment, self-consciousness, and body image issues
Male breast reduction surgery is the most common treatment option, with approximately 24,000 procedures are performed annually worldwide
Prior to the surgery, the patient may undergo various pre-operative tests and evaluations, such as blood tests, imaging studies (e.g., ultrasound), and possibly a mammogram to assess breast tissue composition and rule out any underlying medical conditions.
The surgeon will develop a surgical plan tailored to the patient's specific needs and goals. This may involve determining the extent of tissue removal, the type of surgical technique to be used (e.g., liposuction, excision, or a combination of both), and the location of incisions.
Gynecomastia surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia or local anesthesia with sedation. The surgeon will then proceed with the planned surgical technique to remove excess breast tissue, fat, and skin.
After removing the excess tissue, the surgeon will carefully close the incisions using sutures, adhesive skin closures, or surgical tape.
After the surgery is completed, the patient will be taken to a recovery room, where they will be monitored closely as they wake up from anesthesia. Pain medication and antibiotics may be administered to manage discomfort and reduce the risk of infection.
Patients will receive instructions on how to care for the surgical site, including wound care, wearing compression garments, and avoiding strenuous activities for a specified period.
 Turkey
Turkey Sweden
SwedenLiposuction is a common technique used to remove excess fat from the chest area. During the procedure, small incisions are made, and a thin tube called a cannula is inserted to suction out fat deposits.
Liposuction is particularly effective for treating gynecomastia caused by excess fat accumulation, often resulting in minimal scarring and a relatively quick recovery.
Excision involves the surgical removal of glandular tissue from the chest. This technique is typically used for cases of gynecomastia where glandular tissue enlargement is the primary concern, such as in cases of severe gynecomastia or when liposuction alone is insufficient.
The excision may be performed through periareolar incisions (around the edge of the areola), allowing for direct access to the glandular tissue while minimizing visible scarring.
In some instances, gynecomastia surgery may involve repositioning the nipples to achieve better symmetry and aesthetics.
This may be necessary when there is significant asymmetry or when the nipples are positioned lower on the chest due to excess tissue.
In cases where gynecomastia surgery results in excess skin laxity, additional techniques such as skin tightening may be incorporated into the procedure.
This can help achieve a smoother and more aesthetically pleasing chest contour by removing excess skin and tightening the remaining skin envelope.
The duration of the procedure may differ for each individual, but generally;
1-3 hours
General or Local Anesthesia
1-3 months
Flatter, more masculine chest contour and improved self-confidence.
Liposuction
Candidates for gynecomastia surgery typically include men who experience persistent gynecomastia that does not resolve on its own and who are bothered by the appearance of their chest.
Adolescents with severe gynecomastia, causing significant physical or psychological distress, may also be candidates for surgery after careful evaluation and consultation with medical professionals.
Additionally, healthy individuals with realistic expectations about the outcomes of the procedure, stable weight, and commitment to maintaining a healthy lifestyle are often considered suitable candidates.
Frequently Asked Questions

Explore our informative articles and peruse our blogs for in-depth insights on topics that capture your interest.